Make sure you have django.template.context_processors.request listed in your context_processors.
As of Django 1.9 version, it already comes configurated. The default TEMPLATES configuration looks like that:
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]To get the current path:
{{ request.path }}Current path with querystring:
{{ request.get_full_path }}Domain, path and querystring:
{{ request.build_absolute_uri }}Outputs
Considering we are acessing the following URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/home/?q=test
| Method | Output |
|---|---|
request.path |
/home/ |
request.get_full_path |
/home/?q=test |
request.build_absolute_uri |
http://127.0.0.1:8000/home/?q=test |
Troubleshooting
Django 1.7 or below
If you are using an older version of Django (<= 1.7) where the TEMPLATES configuration is not available, you can include the
context processor like this:
settings.py
from django.conf.global_settings import TEMPLATE_CONTEXT_PROCESSORS as TCP
TEMPLATE_CONTEXT_PROCESSORS = TCP + (
'django.core.context_processors.request',
)Notice the context processor was available inside the core module. Since version >= 1.8 it is available inside the
template module.



 How to Render Django Form Manually
How to Render Django Form Manually
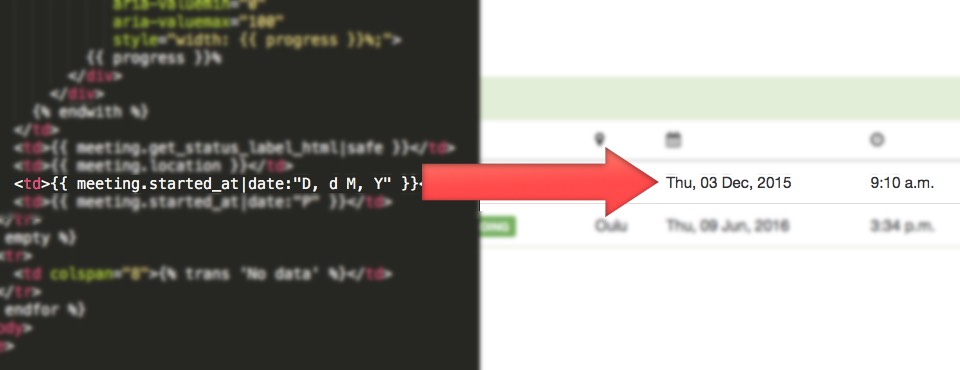 Date Template Filter
Date Template Filter
 How to Extend Django User Model
How to Extend Django User Model
 How to Setup a SSL Certificate on Nginx for a Django Application
How to Setup a SSL Certificate on Nginx for a Django Application
 How to Deploy a Django Application to Digital Ocean
How to Deploy a Django Application to Digital Ocean