Google’s reCAPTCHA is a very popular solution to protect your application or website against bots and spam. It is
fairly simple to implement. In this tutorial you will find a working example using only built-in libraries, an
alternative using requests and also an implementation using decorators, to reuse the reCAPTCHA verification across
your application.
Setup
First thing, register your application in the reCAPTCHA admin.
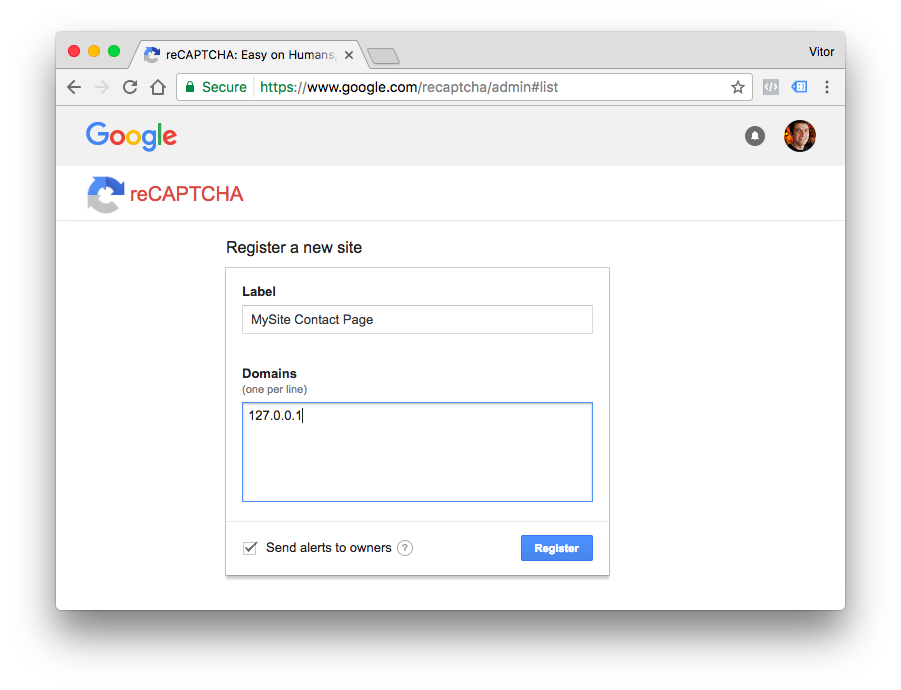
I added the 127.0.0.1 IP address as my domain for testing purpose. Here you are supposed to add your website domain.
After registering your website, you will be handed a Site key and a Secret key. The Site key will be used in the reCAPTCHA widget which is rendered within the page where you want to place it. The Secret key will be stored safely in the server, made available through the settings.py module.
settings.py
GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY = '6LdRSRYUAAAAAOnk5yomm1dI9BmQkJWTg_wIlMJ_'PS: It is not a good idea to keep this kind of information directly in the settings.py. I’m adding it here so the example is more explicit. Please refer to this article Package of the Week: Python Decouple to learn how to separate configuration from settings, and keep sensitive information in a safe place.
Implementing the reCAPTCHA
Let’s say we want to add a reCAPTCHA in a comment section of a website. Inside the form you are currently using to post the data, add the code provided by reCAPTCHA Admin page:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<script src='https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js'></script>
<div class="g-recaptcha" data-sitekey="6LdRSRYUAAAAAFCqQ1aZnYfRGJIlAUMX3qkUWlcF"></div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Post</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}Make sure you change the data-sitekey with the correct key for your website. You may also place the script tag in the
<head> of your template, or in the bottom of the page (depending on how you are organizing the assets).
Just by adding the tags, the reCAPTCHA widget will already show up.
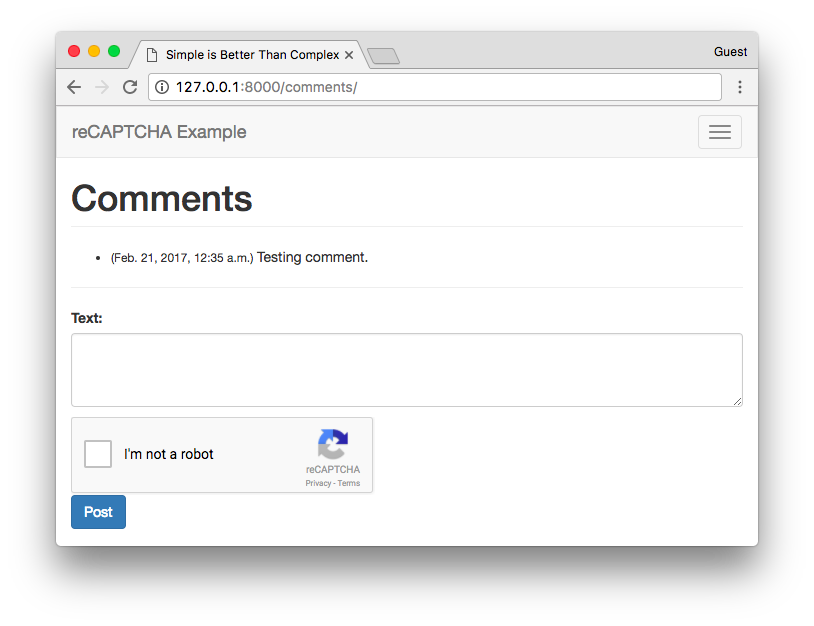
Validating the reCAPTCHA
Next step is to actually validate the data. It is done by making a POST request to the endpoint
https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify, containing your Secret key and the data from the reCAPTCHA
widget, which is identified by g-recaptcha-response.
Python 2 Solution without Third Party Libraries
You can validate it directly in the view function, using just built-in libs:
views.py
import urllib
import urllib2
import json
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib import messages
from .models import Comment
from .forms import CommentForm
def comments(request):
comments_list = Comment.objects.order_by('-created_at')
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
''' Begin reCAPTCHA validation '''
recaptcha_response = request.POST.get('g-recaptcha-response')
url = 'https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify'
values = {
'secret': settings.GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response': recaptcha_response
}
data = urllib.urlencode(values)
req = urllib2.Request(url, data)
response = urllib2.urlopen(req)
result = json.load(response)
''' End reCAPTCHA validation '''
if result['success']:
form.save()
messages.success(request, 'New comment added with success!')
else:
messages.error(request, 'Invalid reCAPTCHA. Please try again.')
return redirect('comments')
else:
form = CommentForm()
return render(request, 'core/comments.html', {'comments': comments_list, 'form': form})Basically result['success'] will return True or False, defining if the reCAPTCHA is valid or not.
Python 3 Solution without Third Party Libraries
views.py
import json
import urllib
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib import messages
from .models import Comment
from .forms import CommentForm
def comments(request):
comments_list = Comment.objects.order_by('-created_at')
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
''' Begin reCAPTCHA validation '''
recaptcha_response = request.POST.get('g-recaptcha-response')
url = 'https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify'
values = {
'secret': settings.GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response': recaptcha_response
}
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(values).encode()
req = urllib.request.Request(url, data=data)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(req)
result = json.loads(response.read().decode())
''' End reCAPTCHA validation '''
if result['success']:
form.save()
messages.success(request, 'New comment added with success!')
else:
messages.error(request, 'Invalid reCAPTCHA. Please try again.')
return redirect('comments')
else:
form = CommentForm()
return render(request, 'core/comments.html', {'comments': comments_list, 'form': form})Alternative Solution With a Third Party Library
If you don’t mind adding an extra dependency, install the requests library:
pip install requestsThen you can make the POST in a relatively easier way:
views.py
import requests
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib import messages
from .models import Comment
from .forms import CommentForm
def comments(request):
comments_list = Comment.objects.order_by('-created_at')
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
''' Begin reCAPTCHA validation '''
recaptcha_response = request.POST.get('g-recaptcha-response')
data = {
'secret': settings.GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response': recaptcha_response
}
r = requests.post('https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify', data=data)
result = r.json()
''' End reCAPTCHA validation '''
if result['success']:
form.save()
messages.success(request, 'New comment added with success!')
else:
messages.error(request, 'Invalid reCAPTCHA. Please try again.')
return redirect('comments')
else:
form = CommentForm()
return render(request, 'core/comments.html', {'comments': comments_list, 'form': form})reCAPTCHA Decorator
This is an extra for this post. This is just an idea of what you can do, to reuse the reCAPTCHA verification code across the project.
decorators.py
from functools import wraps
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib import messages
import requests
def check_recaptcha(view_func):
@wraps(view_func)
def _wrapped_view(request, *args, **kwargs):
request.recaptcha_is_valid = None
if request.method == 'POST':
recaptcha_response = request.POST.get('g-recaptcha-response')
data = {
'secret': settings.GOOGLE_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY,
'response': recaptcha_response
}
r = requests.post('https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify', data=data)
result = r.json()
if result['success']:
request.recaptcha_is_valid = True
else:
request.recaptcha_is_valid = False
messages.error(request, 'Invalid reCAPTCHA. Please try again.')
return view_func(request, *args, **kwargs)
return _wrapped_viewThen you can use it like this:
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib import messages
from .decorators import check_recaptcha
from .models import Comment
from .forms import CommentForm
@check_recaptcha
def comments(request):
comments_list = Comment.objects.order_by('-created_at')
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid() and request.recaptcha_is_valid:
form.save()
messages.success(request, 'New comment added with success!')
return redirect('comments')
else:
form = CommentForm()
return render(request, 'core/comments.html', {'comments': comments_list, 'form': form})That’s about it! Hope you can find it useful somehow. Google’s reCAPTCHA is a very common solution to avoid spam, bots, and can also be used to mitigate brute force attacks on login pages for example.
As usual, all the source code is available on GitHub so you can try it by yourself. Make sure you register your own application to get valid Site key and Secret key.


 (Picture:
(Picture:  Django Tips #19 Protecting Sensitive Information
Django Tips #19 Protecting Sensitive Information
 How to Create a One Time Link
How to Create a One Time Link
 How to Extend Django User Model
How to Extend Django User Model
 How to Setup a SSL Certificate on Nginx for a Django Application
How to Setup a SSL Certificate on Nginx for a Django Application
 How to Deploy a Django Application to Digital Ocean
How to Deploy a Django Application to Digital Ocean